最近刷 leetcode 链表系列刷的头昏脑胀,感觉要写个博客记录一下做链表题的思路。
两大思路 目前链表题做下来,看了这么多题解,可以总结做题有两个方向。
常规思路,迭代,用指针慢慢的找。
递归(递归需要设计的很巧妙)
链表题目可以简单的被分为三大类:
链表的处理
链表的反转以及衍生题目
链表成环问题以及衍生题目
刷题 链表的定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class ListNode { val; next = null ; constructor (value ) { this .val = value; this .next = null ; } }
leetcode 的核心代码模式不需要写链表的定义,但是笔试时是ACM模式,需要自己写链表的定义,这里采用ES6的写法。
移除链表元素 题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
链表的迭代操作有两种方式:
直接使用原来的链表来进行删除操作。 设置一个虚拟头结点在进行删除操作。
直接使用原来的链表来进行删除操作
这里的讲解看代码随想录
https://programmercarl.com/0203.%E7%A7%BB%E9%99%A4%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0.html#%E5%85%B6%E4%BB%96%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E7%89%88%E6%9C%AC
总结:直接使用原来的链表需要考虑删除头节点的情况(跟删除别的节点逻辑不一样,需要单独写一段逻辑),使用虚拟头节点的方式更简单,在返回的时候不要忘了 return dummyNode->next; 。这才是新的头节点。
展示我自己的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 var removeElements2 = function (head, val ) { if (head == null ) return null ; while (head != null && head.val === val) { head = head.next ; } let cur = head; while (cur != null && cur.next != null ) { if (cur.next .val == val) { cur.next = cur.next .next ; } else { cur = cur.next ; } } return head; };
设置一个虚拟头结点在进行删除操作。
这个方法统一逻辑,代码更简单
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 var removeElements = function (head, val ) { let header = new ListNode (0 , null ); header.next = head; let cur = header; while (cur.next != null ) { if (cur.next .val === val) { cur.next = cur.next .next ; } else { cur = cur.next ; } } return header.next ; };
(*)设计链表 题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-linked-list/
这道题目设计链表的五个接口:
获取链表第index个节点的数值
在链表的最前面插入一个节点
在链表的最后面插入一个节点
在链表第index个节点前面插入一个节点
删除链表的第index个节点
因为这是一个整体的代码,就不要使用虚拟头节点,因为很多节点操作不需要return header.next;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 class ListNode { val; next = null ; constructor (value ) { this .val = value; this .next = null ; } } var MyLinkedList = function ( this .length = 0 ; this .tail = null ; this .head = null ; }; MyLinkedList .prototype get = function (index ) { if (index < 0 || index >= this .length ) return ; let cur = this .head ; for (let i = 0 ; i < index; i++) { cur = cur.next ; } return cur.val ; }; MyLinkedList .prototype addAtHead = function (val ) { let node = new ListNode (val); this .length ++; node.next = this .head ; this .head = node; if (!this .tail ) { this .tail = node; } }; MyLinkedList .prototype addAtTail = function (val ) { let node = new ListNode (val); this .length ++; this .tail .next = node; this .tail = node; if (!this .head ) { this .head = node; } }; MyLinkedList .prototype addAtIndex = function (index, val ) { if (index < 0 || index >= this .length ) return ; let node = new ListNode (val); if (index == 0 ) { node.next = this .head ; this .head = node; } else { let cur = this .head ; for (let i = 0 ; i < index - 1 ; i++) { cur = cur.next ; } node.next = cur.next ; cur.next = node; } this .length ++; }; MyLinkedList .prototype deleteAtIndex = function (index ) { if (index <= 0 || index > this .length ) return ; let cur = this .head ; if (index == 1 ) { this .head = this .head .next ; } else { for (let i = 0 ; i < index - 2 ; i++) { cur =cur.next ; } cur.next = cur.next .next ; } };
(*)反转链表(简单) 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
两个思路:
定义一个新链表,实现链表的反转,但是浪费空间
双指针法,具体思路看图(参考代码随想录)
头插法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 var reverseList = function (head ) { let header = new ListNode (0 , null ); while (head != null ) { let cur = head; head = head.next ; cur.next = header.next ; header.next = cur; } return header.next ; };
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 var reverseList = function (head ) { let pre = null ; let cur = head; let temp = null ; while (cur != null ) { temp = cur.next ; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; };
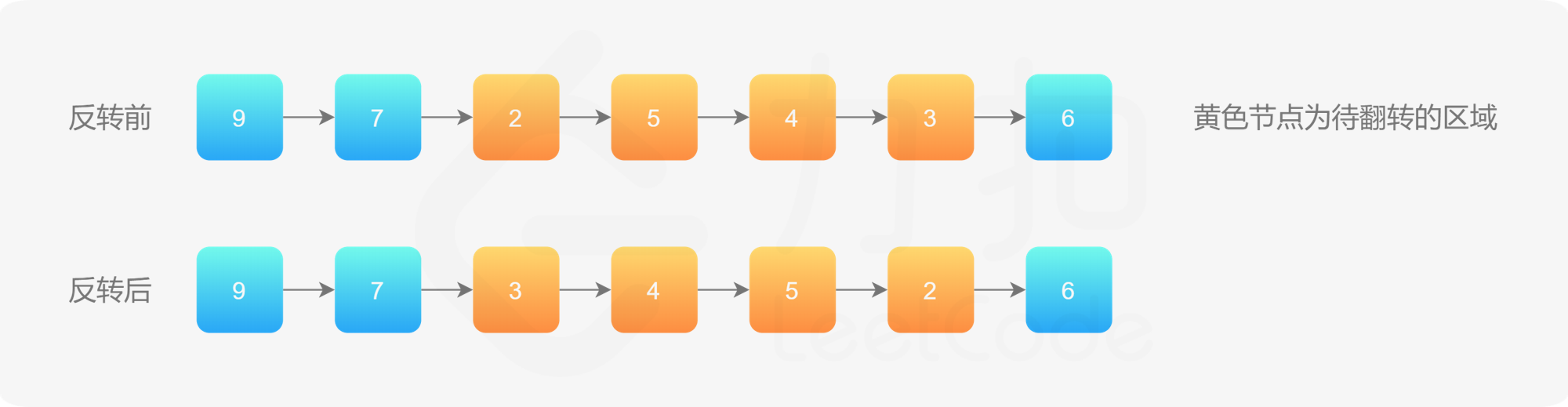
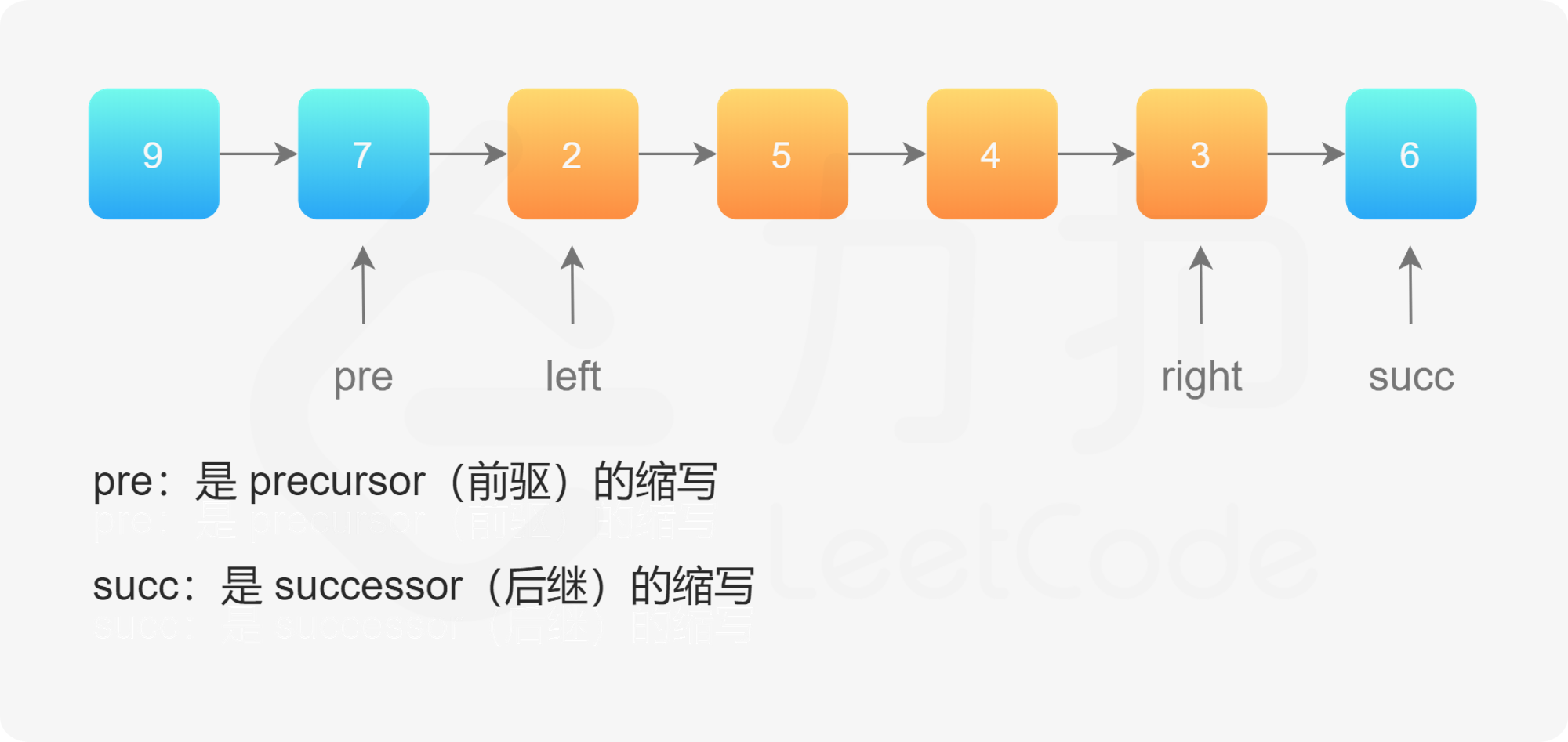
反转链表2 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/
这题一开始不怎么会写,看了官方题解,讲的很好。
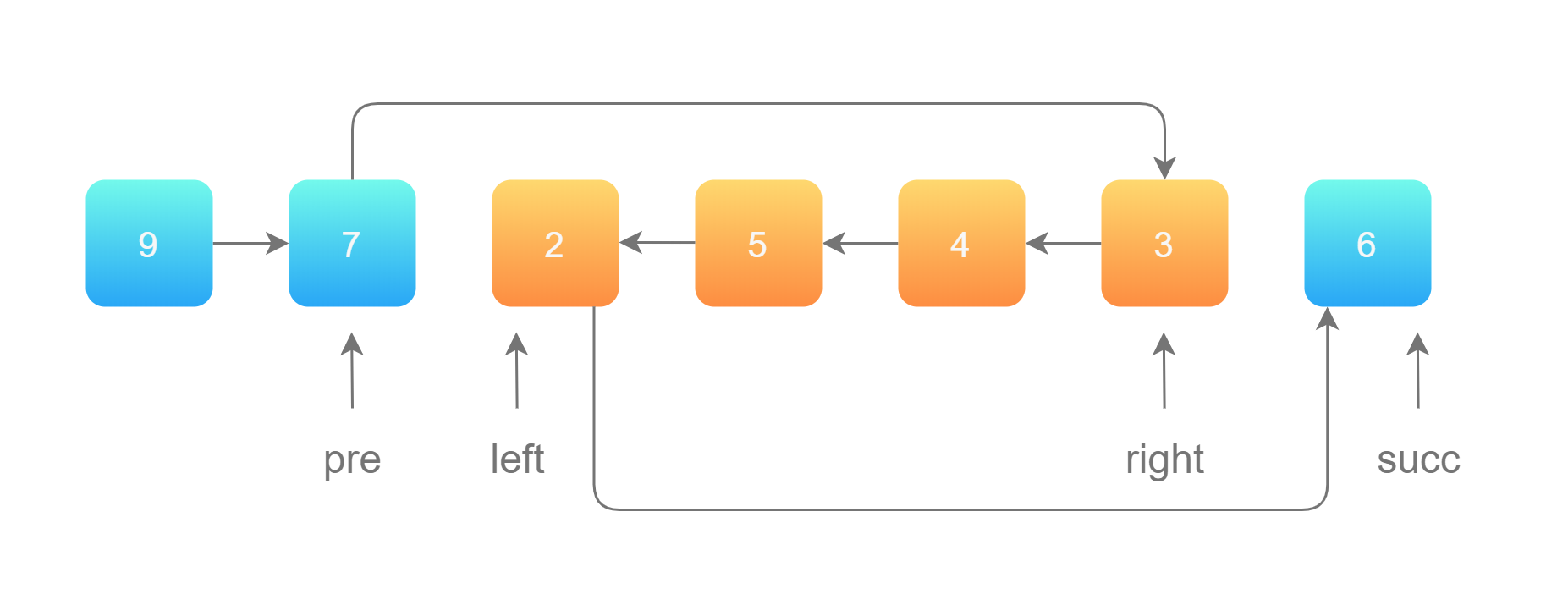
方法:穿针引线
使用上一题的解法,反转 left 到 right 部分以后,再拼接起来。我们还需要记录 left 的前一个节点,和 right 的后一个节点。如图所示:
算法步骤:
第 1 步:先将待反转的区域反转;
代码:(仔细反复看)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 var reverseBetween = function (head, left, right ) { let dummyNode = new ListNode (-1 ); dummyNode.next = head; let pre = dummyNode; for (let i = 0 ; i < left - 1 ; i++) { pre = pre.next ; } let rightNode = pre; for (let i = 0 ; i < right - left + 1 ; i++) { rightNode = rightNode.next ; } let leftNode = pre.next ; let curr = rightNode.next ; pre.next = null ; rightNode.next = null ; let reverse = reverseList (leftNode); pre.next = reverse; leftNode.next = curr; return dummyNode.next }; var reverseList = function (head ) { let pre = null ; let cur = head; let temp = null ; while (cur != null ) { temp = cur.next ; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; };
合并两个有序链表 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
这题自己也用普通方法写出来了,和官方题解一比就太垃圾了,所以参考官方题解修改答案
递归比较麻烦,使用迭代比较简单,能A就行。。
这题不难,但是理解的话看官方的图更好
地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/solution/he-bing-liang-ge-you-xu-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solu/
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2 ) { let prehead = new ListNode (-1 ); let prev = prehead; let l1 = list1; let l2 = list2; while (l1 != null && l2 != null ) { if (l1.val <= l2.val ) { prev.next = l1; prev = l1; l1 = l1.next ; } else { prev.next = l2; prev = l2; l2 = l2.next ; } } prev.next = l1 === null ? l2 : l1; return prehead.next };
删除排序链表中的重复元素 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
思路:由于给定的链表是排好序的,因此重复的元素在链表中出现的位置是连续的 ,因此我们只需要对链表进行一次遍历,就可以删除重复的元素。
具体地,我们从指针 cur 指向链表的头节点,随后开始对链表进行遍历。如果当前 cur 与 cur.next 对应的元素相同,那么我们就将 cur.next 从链表中移除;否则说明链表中已经不存在其它与 cur 对应的元素相同的节点,因此可以将cur 指向 cur.next。
当遍历完整个链表之后,我们返回链表的头节点即可。
注意:
当我们遍历到链表的最后一个节点时,\textit{cur.next}cur.next 为空节点,如果不加以判断,访问 cur.next 对应的元素会产生运行错误。因此我们只需要遍历到链表的最后一个节点
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 var deleteDuplicates = function (head ) { if (head === null ) { return null ; } let cur = head; while (cur.next != null ) { if (cur.val === cur.next .val ) { cur.next = cur.next .next ; } else { cur = cur.next ; } } return head; };
删除排序链表中的重复元素2 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/
思路:
还是比较简单的。
由于给定的链表是排好序的,因此重复的元素在链表中出现的位置是连续的,因此我们只需要对链表进行一次遍历,就可以删除重复的元素。由于链表的头节点可能会被删除,因此我们需要额外使用一个哑节点(dummy node)指向链表的头节点。
具体地,我们从指针 cur 指向链表的哑节点,随后开始对链表进行遍历。如果当前 cur.next 与 cur.next.next 对应的元素相同,那么我们就需要将 cur.next 以及所有后面拥有相同元素值的链表节点全部删除。我们记下这个元素值 x,随后不断将 cur.next 从链表中移除,直到 cur.next 为空节点或者其元素值不等于 x 为止。此时,我们将链表中所有元素值为 x 的节点全部删除。
注意:
如果当前 cur.next.next 对应的元素不相同,那么说明链表中只有一个元素值为 cur.next 的节点,那么我们就可以将 cur 指向 cur.next。
当遍历完整个链表之后,我们返回链表的的哑节点的下一个节点 dummy.next 即可。
需要注意 cur.next 以及 cur.next.next 可能为空节点,如果不加以判断,可能会产生运行错误。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 var deleteDuplicates = function (head ) { if (!head) { return head; } let dummy = new ListNode (-1 , head); let cur = dummy; while (cur.next != null && cur.next .next != null ) { if (cur.next .val === cur.next .next .val ) { let x = cur.next .val ; while (cur.next != null && cur.next .val === x) { cur.next = cur.next .next ; } } else { cur = cur.next ; } } return dummy.next ; };
删除链表中的节点 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
这题有点脑筋急转弯的意思。。。
笔试绝对不会有这种题的感觉。。。
放个官方思路链接:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/solution/shan-chu-lian-biao-zhong-de-jie-dian-by-x656s/
代码:
1 2 3 4 var deleteNode = function (node ) { node.val = node.next .val ; node.next = node.next .next ; };
删除链表的倒数第 N 个节点 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
思路:
这题就是经典前后指针的应用。
如果要删除倒数第n个节点,让fast移动n步,然后让fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向链表末尾。删掉slow所指向的节点就可以了。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n ) { let dummy = new ListNode (-1 , head); let first = dummy; let second = dummy; for (let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { first = first.next ; } while (first.next != null ) { first = first.next ; second = second.next ; } second.next = second.next .next ; return dummy.next ; };
两两交换链表中的节点 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
思路:
这题链表交换比较复杂,需要画图理解。
可以看官方题解的图(很详细)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/solution/liang-liang-jiao-huan-lian-biao-zhong-de-jie-di-91/
核心逻辑:
第一步:设置一个哑节点。设立temp指针指向哑节点,temp指针后面设置node1和node2指针。
1 2 3 temp = dummyHead; node1 = temp.next ; node2 = temp.next .next ;
第二步:原来是 dummy —-> 1 —–> 2。现在要改成 dummy —-> 2 —-> 1,所以 temp的 next 要先指向 node2, node2 的 next 要指向 node1, node1 的 next 要 指向 3。
1 2 3 temp.next = node2; node1.next = node2.next; node2.next = node1;
第三步:这一轮结束后,让 temp 指向 node1, node1 为 temp.next,node2 为 temp.next.next。
1 2 3 temp = node1; node1 = temp.next ; node2 = temp.next ;
接下来就重复第二步就行了。
结束条件:
如果 temp 的后面没有节点或者只有一个节点,则没有更多的节点需要交换,因此结束交换。
完整代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 var swapPairs = function (head ) { let dummy = new ListNode (-1 , head); let temp = dummy; while (temp.next != null && temp.next .next != null ) { let node1 = temp.next ; let node2 = temp.next .next ; temp.next = node2; node1.next = node2.next ; node2.next =node1; temp = node1; } return dummy.next ; };
链表相交 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/
思路:
题目没怎么看懂,就按照代码随想录的来写了。。。(感觉面试笔试应该也不会考的吧。。。)
看如下两个链表,目前curA指向链表A的头结点,curB指向链表B的头结点:
我们求出两个链表的长度,并求出两个链表长度的差值,然后让curA移动到,和curB 末尾对齐的位置,如图:
此时我们就可以比较curA和curB是否相同,如果不相同,同时向后移动curA和curB,如果遇到curA == curB,则找到交点。
否则循环退出返回空指针。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 var getListLen = function (head ) { let len = 0 ; let cur = head; while (cur != null ) { len++; cur = cur.next ; } return len; } var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB ) { let curA = headA; let curB = headB; let lenA = getListLen (headA); let lenB = getListLen (headB); if (lenA < lenB) { let tempLen = lenB; lenB = lenA; lenA = tempLen; let tempNode = curB; curB = curA; curA = tempNode; } let len = lenA - lenB; for (let i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { curA = curA.next ; } while (curA != null && curA !== curB) { curA = curA.next ; curB = curB.next ; } return curA; };
环形链表 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
思路:
这题比较简单:
两个方法解决
哈希表:最容易想到的方法是遍历所有节点,每次遍历到一个节点时,判断该节点此前是否被访问过。
快慢指针:因为存在环,所以快指针一定会追上慢指针
哈希表解决:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var hasCycle = function (head ) { let set = new Set (); while (head) { if (set.has (head)) { return true ; } set.add (head); head = head.next ; } return false ; };
快慢指针解决:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 var hasCycle = function (head ) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) return false ; let slow = head; let fast = head.next ; while (slow != fast) { if (fast == null || fast.next == null ) { return false ; } slow = slow.next ; fast = fast.next .next ; } return true ; };
环形链表2 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
这题跟上一题一样,两个方法,只是这题要记录下如环的第一个节点
哈希表解决:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var detectCycle = function (head ) { let set = new Set (); while (head) { if (set.has (head)) { return head; } set.add (head); head = head.next ; } return null ; };
快慢指针思路:
公式推理看:https://programmercarl.com/0142.%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8II.html#%E6%80%9D%E8%B7%AF
结论:当快节点和慢节点在环内相遇时,设置一个节点prev 指向头,然后和慢节点一起移动,最后这两个节点相遇的地方就是环的入口。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 var detectCycle = function (head ) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) return null ; let slow = head; let fast = head; while (fast != null ) { slow = slow.next ; if (fast.next != null ) { fast = fast.next .next ; } else { return null ; } if (fast === slow) { let prev = head; while (prev != slow) { prev = prev.next ; slow = slow.next ; } return prev; } } return null ; };